Webscraping with RSelenium and rvest
In this post I’ll talk about the RSelenium package as a tool to navigate websites and how it can be combined with the rvest package to scrape dynamic web pages. To understand this post, you’ll need basic knowledge of rvest, HTML and CSS. You can download the full R script HERE!
Observation: Even if you are not familiar with them, I explained as much as possible everything I did. For that reason, those who know about this stuff might find some parts of the post redundant. Feel free to read what you need and skip what you aldeady know!
Static vs Dynamic Web Pages
Let’s compare the following websites:
On IMDb, if you search for a particular movie (for example, this one), you can see that the URL changes, and that URL is different from any other movie (for example, this one). The same behavior is shown if you search for different actors.
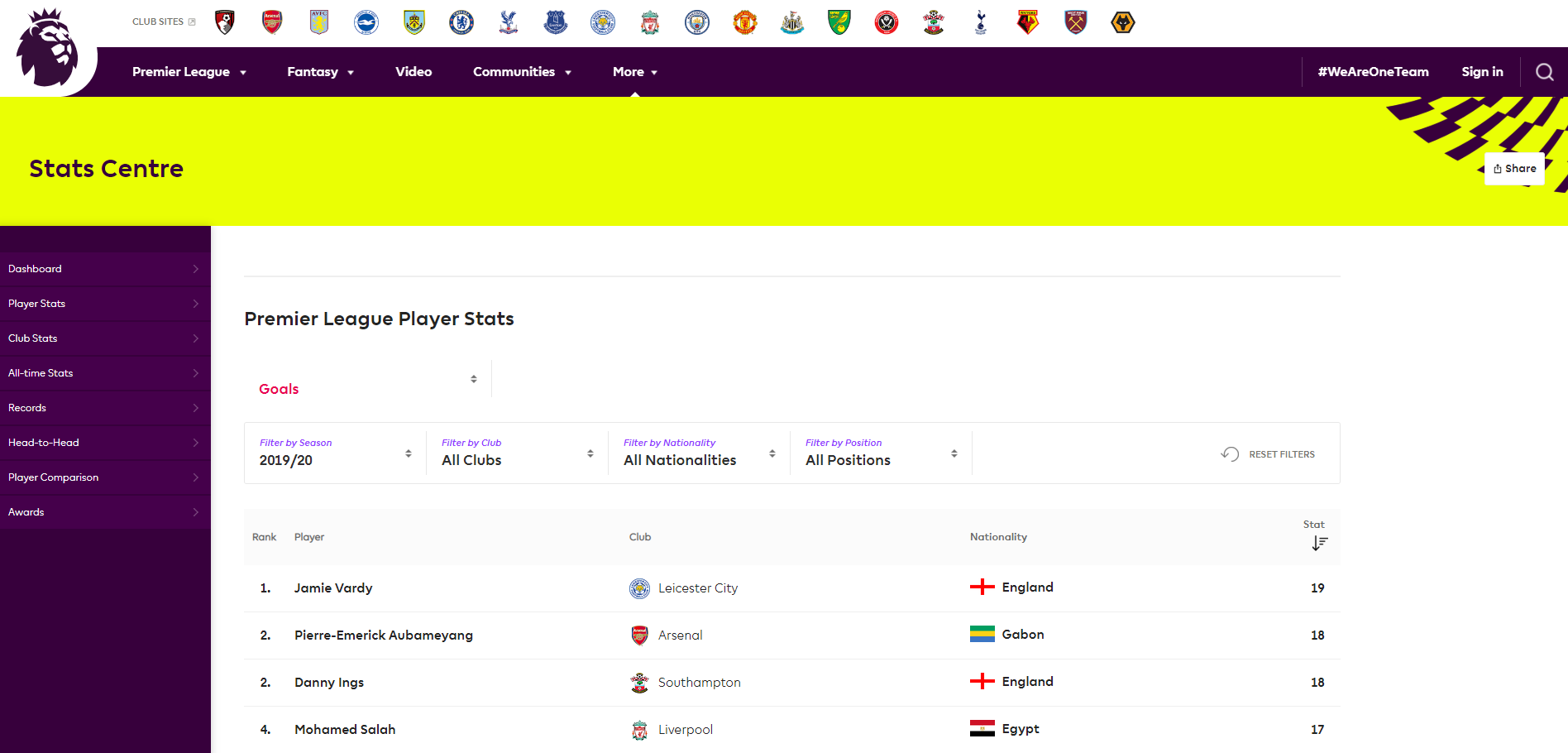
On the other hand, if you go to Premier League Player Stats, you will notice that modifying the filters or clicking the pagination button to access more data doesn’t produce changes on the URL.
As I understand it, the first website is an example of a static web page, while the second one is an example of a dynamic webpage.
The following definitions where taken from https://www.pcmag.com/.
Static Web Page: A Web page (HTML page) that contains the same information for all users. Although it may be periodically updated from time to time, it does not change with each user retrieval.
Dynamic Web Page: A Web page that provides custom content for the user based on the results of a search or some other request. Also known as “dynamic HTML” or “dynamic content”, the “dynamic” term is used when referring to interactive Web pages created for each user.
rvest is a great tool to scrape data from static web pages (check out Creating a Movies Dataset to see an example!).
But when it comes to dynamic web pages, rvest alone can’t get the job done. This is when RSelenium joins the party…
Prerequisites
Java
You need to have Java installed. You can use Windows’ Command Prompt to check this. Just type java -version and press Enter. You should see something that looks like this:
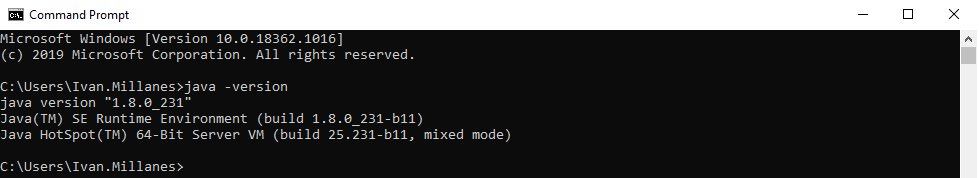
If it throws an error, it might mean that you don’t have Java installed. You can download it from HERE.
R Packages
The following packages need to be installed and loaded in order to run the code written in this post.
library(tidyverse)
library(rvest)
library(RSelenium)Start Selenium
Starting a Selenium server and browser is pretty straightforward using rsDriver().
rD <- RSelenium::rsDriver()However, when you run the code above it may produce the following error:
Selenium message:session not created: This version of ChromeDriver only supports Chrome version 85
...This error is addressed in this StackOverflow post. Basically, it means that there is a mismatch between the ChromeDriver and the Chrome Browser versions. As mentioned in the post, each version of ChromeDriver supports Chrome with matching major, minor, and build version numbers. For example, ChromeDriver 73.0.3683.20 supports all Chrome versions that start with 73.0.3683.
The parameter chromever defined this way always uses the latest compatible ChromeDriver version (the code was edited from this StackOverflow post).
# Start Selenium server and browser
rD <- RSelenium::rsDriver(
browser = "chrome",
chromever =
# Get Chrome version
system2(
command = "wmic",
args = 'datafile where name="C:\\\\Program Files (x86)\\\\Google\\\\Chrome\\\\Application\\\\chrome.exe" get Version /value',
stdout = TRUE,
stderr = TRUE
) %>%
# Wrangling
stringr::str_extract(pattern = "(?<=Version=)\\d+\\.\\d+\\.\\d+\\.") %>%
magrittr::extract(!is.na(.)) %>%
stringr::str_replace_all(pattern = "\\.", replacement = "\\\\.") %>%
paste0("^", .) %>%
# Match versions
stringr::str_subset(
# List chromedriver versions
string = binman::list_versions(appname = "chromedriver") %>% unlist()
)
)
# Assign the client to an object
remDr <- rD[["client"]]After you run rD <- RSelenium::rsDriver(...), if everything worked correctly, a new chrome window will open. This window should look like this:
You can find more information about rsDriver() in the Basics Vignette.
Basic Usage
In this section I’ll apply different methods to the remDr object created above. I’m only going to describe the methods that I think will be used most frequently. For a complete reference, check the package documentation.
navigate(url): Navigate to a given url.
remDr$navigate("https://www.google.com/")
remDr$navigate("https://www.nytimes.com/")
# Use method without () to get a description of what it does
remDr$navigategoBack(): Equivalent to hitting the back button on the browser.goForward(): Equivalent to hitting the forward button on the browser.
remDr$goBack()
remDr$goForward()refresh(): Reload the current page.
remDr$refresh()getCurrentUrl(): Retrieve the url of the current page.
remDr$getCurrentUrl()maxWindowSize(): Set the size of the browser window to maximum. By default, the browser window size is small, and some elements of the website you navigate to might not be available right away (I’ll talk more about this in the next section).
remDr$maxWindowSize()getPageSource()[[1]]Get the current page source. This method combined withrvestis what makes possible to scrape dynamic web pages. The xml document returned by the method can then be read usingrvest::read_html(). This method returns alistobject, that’s the reason behind[[1]].
remDr$getPageSource()[[1]]open(silent = FALSE): Send a request to the remote server to instantiate the browser. I use this method when the browser closes for some reason (for example, inactivity). If you have already started the Selenium server, you should run this instead ofrD <- RSelenium::rsDriver(...)to re-open the browser.
remDr$open()close(): Close the current session.
remDr$close()Working with Elements
findElement(using, value). Search for an element on the page, starting from the document root. The located element will be returned as an object of webElement class. To use this function you need some basic knowledge of HTML and CSS (or xpath, etc). This chrome extension, called SelectorGadget, might help.highlightElement(): Utility function to highlight current Element. This helps to check that you selected the wanted element.sendKeysToElement(): Send a sequence of key strokes to an element. The key strokes are sent as a list. Plain text is enter as an unnamed element of the list. Keyboard entries are defined in ‘selKeys‘ and should be listed with name ‘key‘.clearElement(): Clear a TEXTAREA or text INPUT element’s value.clickElement(): Click the element. You can click links, check boxes, dropdown lists, etc.
# Navigate to Google
remDr$navigate("https://www.google.com/")
# Find search box
webElem <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector", value = ".gLFyf.gsfi")
# Highlight to check that was correctly selected
webElem$highlightElement()
# Send search and press enter
# Option 1
webElem$sendKeysToElement(list("the new york times"))
webElem$sendKeysToElement(list(key = "enter"))
# Option 2
webElem$sendKeysToElement(list("the new york times", key = "enter"))
# Go back to Google
remDr$goBack()
# Search something else
webElem$sendKeysToElement(list("finantial times"))
# Clear element
webElem$clearElement()
# Search and click
webElem <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector", value = ".gLFyf.gsfi")
webElem$sendKeysToElement(list("the new york times", key = "enter"))
webElem <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector", value = ".LC20lb.DKV0Md")
webElem$clickElement()Other Methods
Even though I have never used them, I believe this methods are worth mentioning. For more information, check the package documentation.
remDr$getStatus()
remDr$getTitle()
remDr$screenshot()
remDr$getWindowSize()
remDr$setWindowSize(1000,800)
remDr$getWindowPosition()
remDr$setWindowPosition(100, 100)
webElem$getElementLocation()Example: Webscraping Premier League Player Stats
In this example, I’ll scrape data from Premier League Player Stats. This is what the website looks like:
You will notice that when you modify the Filters, the URL does not change. So you can’t use rvest alone to dynamically scrape this website. Also, if you scroll down to the end of the table you’ll see that there are pagination buttons. If you click them, you get more data, but again, the URL does not change. Here you can see how those pagination buttons look like:
Observation: Even though choosing a different stat does change the URL, I’ll work as if it didn’t.
Target Dataset
The dataset I want will have the following variables:
- Player: Indicates the player name.
- Nationality: Indicates the nationality of the player.
- Season: Indicates the season the stats corresponds to.
- Club: Indicates the club the player belonged to in the season.
- Position: Indicates the player position in the season.
- Stats: One column for each Stat.
For simplicity, I’ll scrape data from seasons 2017/18 and 2018/19, and only from the Goals, Assists, Minutes Played, Passes, Shots and Fouls stats. This means that our dataset will have a total of 11 columns.
Before we start…
In order to run the code below, you have to start a Selenium server and browser, and create the remDr object. This procedure was described in the Start Selenium section.
First Steps
The code chunk below navigates to the website, increases the windows size to find elements that might be hidden (for example, when the window is small I can’t see the Filters) and then clicks the “Accept Cookies” button.
You might notice two things:
The use of the
Sys.sleep()function. Here, this function is used to give the website enough time to load. Sometimes, if the element you want to find isn’t loaded when you search for it, it will produce an error.The use of CSS selectors. To select an element using CSS you can press F12 an inspect the page source (right clicking the element and selecting Inspect will show you which part of that code refers to the element) and/or use this chrome extension, called SelectorGadget. I recommend learning a little about HTML and CSS and use this two approaches simultaneosly. SelectorGadget helps, but sometimes you will need to inspect the source to get exactly what you want. In the next subsection I’ll show how I selected certain elements by inspecting the page source.
# Navigate to the website
remDr$navigate("https://www.premierleague.com/stats/top/players/goals?se=274")
# Give some time to load
Sys.sleep(4)
# Increase window size to find elements
remDr$maxWindowSize()
# Accept cookies
acceptCookies <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = "div[class='btn-primary cookies-notice-accept']")
acceptCookies$clickElement()Getting Values to Iterate Over
I know that in order to get the data, I’ll have to iterate over different lists of values. In particular, I need a list of stats, seasons, and player positions.
We can use rvest to scrape the website and get these lists. To do so, we need to find the corresponding nodes. As an example, after the code I’ll show where I searched for the required information in the page source for the stats and seasons lists.
The code below uses rvest to create the lists we’ll use in the loops.
# Read page source
source <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]]
# Get topStats
list_topStats <- read_html(source) %>%
html_nodes(".topStatsLink") %>%
html_text() %>%
str_trim() %>%
str_to_title() # Observation below.
# To make example simple
list_topStats <- list_topStats[c(1, 2, 5, 8, 10, 15)]
# Get seasons
list_seasons <- read_html(source) %>%
html_nodes("ul[data-dropdown-list=FOOTBALL_COMPSEASON] > li") %>%
html_attr("data-option-name") %>%
.[-1] # Remove "All seasons" option
# To make example simple
list_seasons <- list_seasons[c(2,3)]
# Get positions
list_positions <- read_html(source) %>%
html_nodes("ul[data-dropdown-list=Position] > li") %>%
html_attr("data-option-id") %>%
.[-1] # Remove "All positions" optionObservation: Even though in the source we don’t see that each word has its first letter
uppercased, when we check the dropdown list we see exactly that (for example, we have “Clean Sheets” instead of “Clean sheets”). I was getting an error when trying to scrape these type of stats, and making them look like the dropdown list solved the issue. That’s the reason behind str_to_title().
Stats
This is my view when I open the stats dropdown list and right click and inspect the Clean Sheets stat.
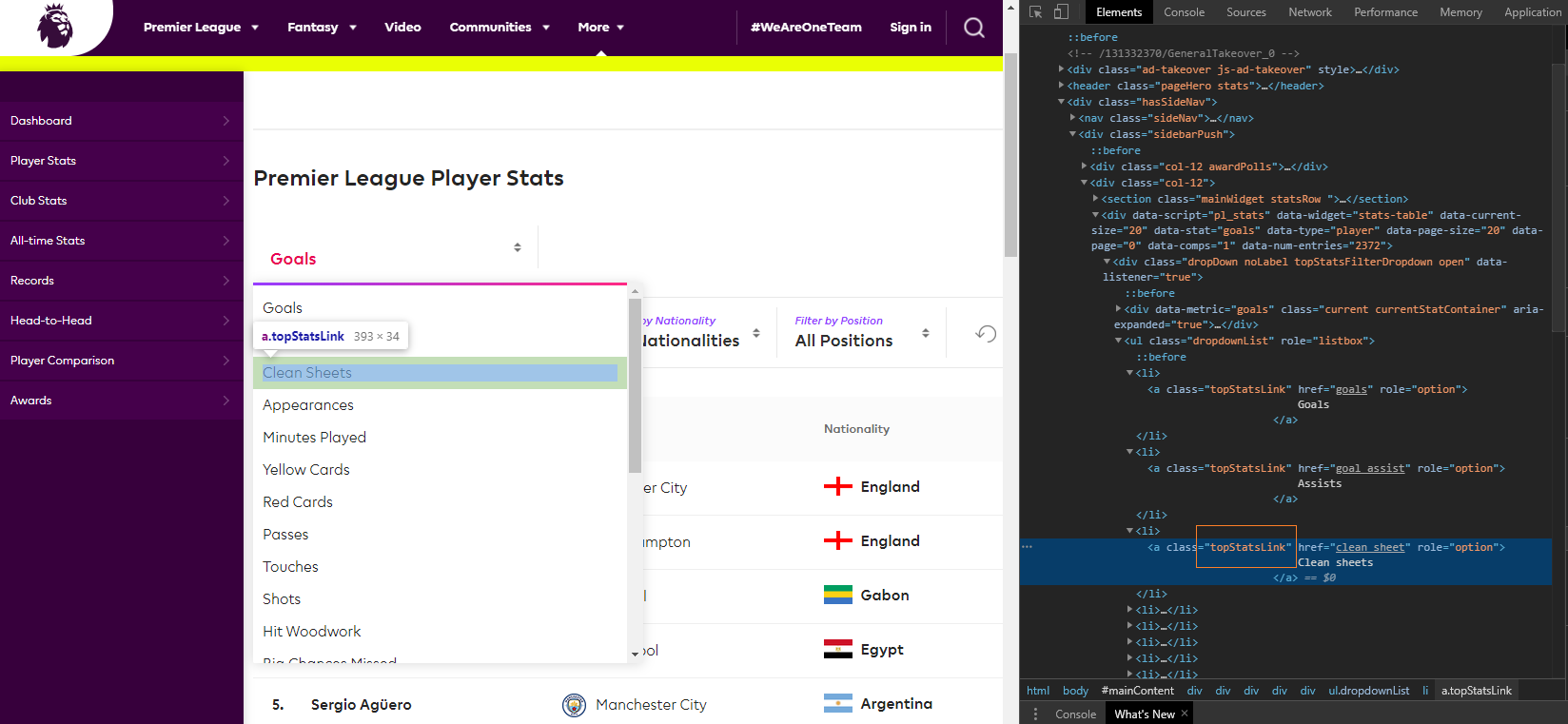
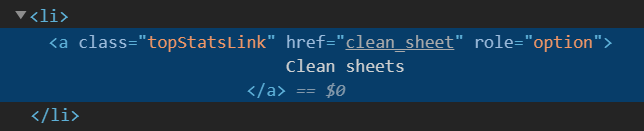
Taking a closer look to the source where that element is present we get:
Seasons
This is my view when I open the seasons dropdown list and right click and inspect the 2016/17 season.
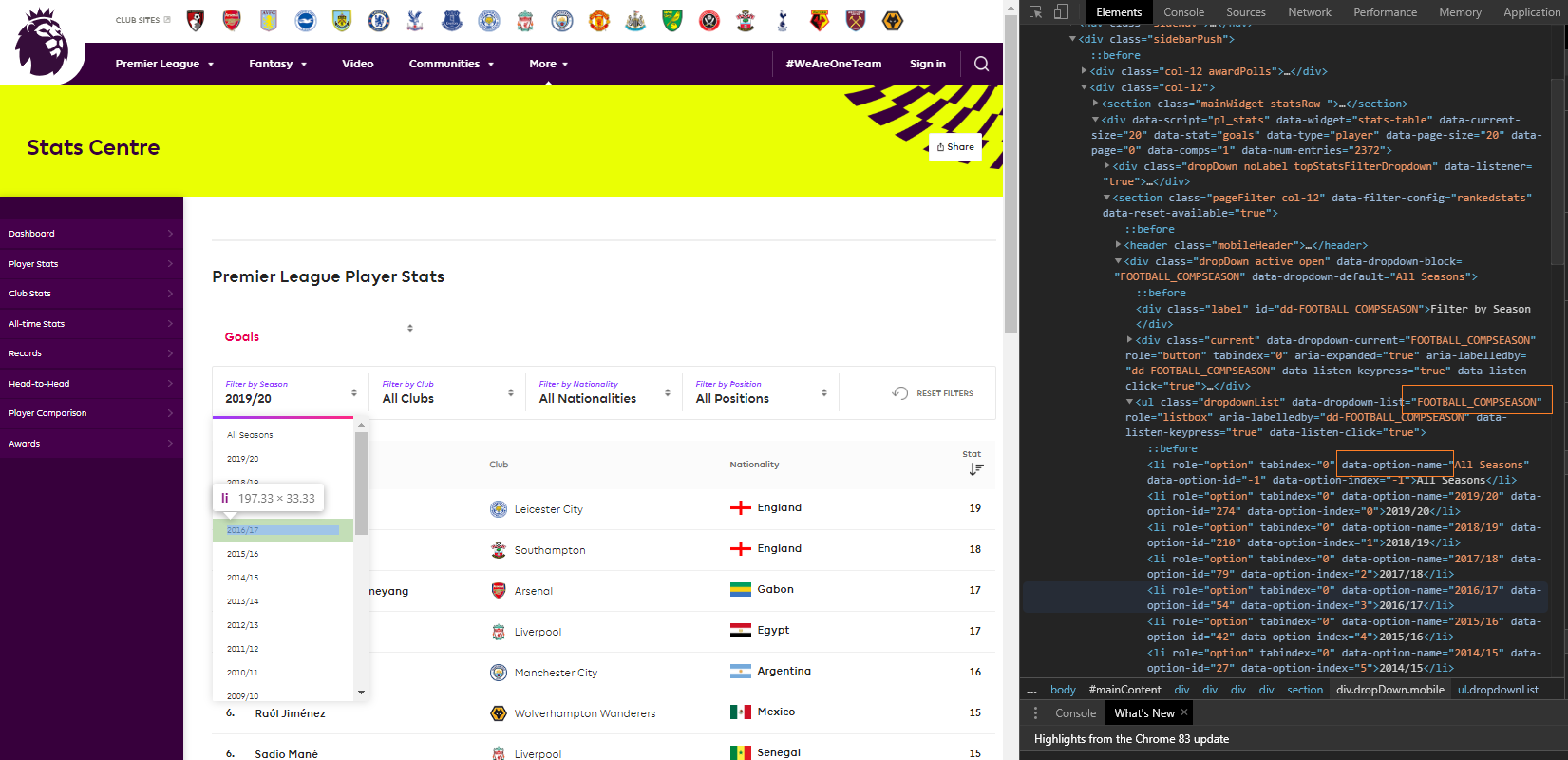
Taking a closer look to the source where that element is present we get:
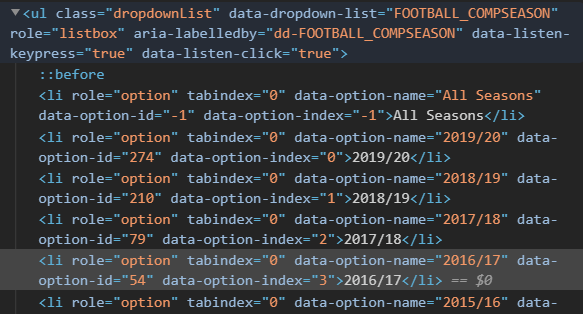
As you can see, we have an attribute named data-dropdown-list whose value is FOOTBALL_COMPSEASON and inside we have li tags where the attribute data-option-name changes for each season. This will be useful when defining how to iterate using RSelenium.
Positions
The logic behind getting the CSS for the positions is similar to the one described above, so I won’t be showing it.
Webscraping Loop
The code has comments on each step, so you can check it out! But before that, I’ll give an overview of the loop.
Preallocate stats vector. This list will have a length equal to the number of stats to be scraped.
For each stat:
- Click the stat dropdown list
- Click the corresponding stat
- Preallocate seasons vector. This list will have a length equal to the number of seasons to be scraped.
- For each season inside stat:
- Click the seasons dropdown list
- Click the corresponding season
- Preallocate positions vector. This list will have
length = 4(positions are fixed: GOALKEEPER, DEFENDER, MIDFIELDER and FORWARD). - For each position inside season inside stat
- Click the position dropdown list
- Click the corresponding position
- Check that there is a table with data (if not, go to next position)
- Scrape the first table
- While “Next Page” button exists
- Click “Next Page” button
- Scrape new table
- Append new table to table
- Change stat colname and add position data
- Go to the top of the website
- Rowbind each position table
- Add season data
- Rowbind each season table
- Assign the table to the corresponding stat element.
The result of this loop is a populated list with a number of elements equal to the number of stats scraped. Each of this elements is a tibble.
This may take some time to run, so you can choose less stats to try it out.
As I mentioned, you can check the code!
# Preallocate vector
data_topStats <- vector("list", length(list_topStats))
# Iterate over topStat
for (i in seq_along(list_topStats)){
# Open topStat dropdown list
DDLtopStat <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = ".dropDown.noLabel.topStatsFilterDropdown")
DDLtopStat$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Click corresponding topStat
ELEMtopStat <- remDr$findElement(using = "link text",
value = list_topStats[[i]])
ELEMtopStat$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Preallocate vector
data_seasons <- vector("list", length(list_seasons))
# Iterate over seasons
for (j in seq_along(list_seasons)){
# Open seasons dropdown list
DDLseason <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = ".current[data-dropdown-current=FOOTBALL_COMPSEASON]")
DDLseason$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Click corresponding season
ELEMseason <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = str_c("ul[data-dropdown-list=FOOTBALL_COMPSEASON] > li[data-option-name='", list_seasons[[j]], "']"))
ELEMseason$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Preallocate vector
data_positions <- vector("list", length(list_positions))
# Iterate over position
for (k in seq_along(list_positions)){
# Open positions dropdown list
DDLposition <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = ".current[data-dropdown-current=Position]")
DDLposition$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Click corresponding position
ELEMposition <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = str_c("ul[data-dropdown-list=Position] > li[data-option-id='", list_positions[[k]], "']"))
ELEMposition$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Check that there is a table to scrape. If there isn't, go to next position
check_table <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]] %>%
read_html() %>%
html_node(".statsTableContainer") %>%
html_text()
if(check_table == "No stats are available for your search") next
# Populate element of corresponding position (first page)
data_positions[[k]] <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]] %>%
read_html() %>%
html_table() %>%
.[[1]] %>%
as_tibble() %>%
# Thousands are character ("1,000"), problem when binding with integer (1:999)
mutate(Stat = as.character(Stat) %>%
parse_number())
# Get tables from every page
btnNextExists <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]] %>%
read_html() %>%
html_node(".paginationNextContainer.inactive") %>%
html_text() %>%
is.na()
# While there is a Next button to click
while (btnNextExists){
# Click "Next"
btnNext <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector",
value = ".paginationNextContainer")
btnNext$clickElement()
Sys.sleep(2)
# Get table from new page
table_n <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]] %>%
read_html() %>%
html_table() %>%
.[[1]] %>%
as_tibble() %>%
mutate(Stat = as.character(Stat) %>%
parse_number())
#Rowbind existing table and new table
data_positions[[k]] <- bind_rows(data_positions[[k]], table_n)
# Update Check for Next Button
btnNextExists <- remDr$getPageSource()[[1]] %>%
read_html() %>%
html_node(".paginationNextContainer.inactive") %>%
html_text() %>%
is.na()
Sys.sleep(1)
}
# Data wrangling
data_positions[[k]] <- data_positions[[k]] %>%
rename(!!list_topStats[[i]] := Stat) %>%
mutate(Position = list_positions[[k]])
# Go to top of the page to select next position
goTop <- remDr$findElement("css", "body")
goTop$sendKeysToElement(list(key = "home"))
Sys.sleep(3)
}
# Rowbind positions dataset
data_positions <- reduce(data_positions, bind_rows)
# Populate corresponding season
data_seasons[[j]] <- data_positions %>%
mutate(Season = list_seasons[[j]])
}
# Rowbind seasons dataset
data_seasons <- reduce(data_seasons, bind_rows)
# Populate corresponding topStat
data_topStats[[i]] <- data_seasons
}Observation: Be careful when you add more stats to the loop. For example, Clean Sheets has the Position filter hidden, so the code should be modified (for example, by adding some “if” statement).
Data Wrangling
Finally, some data wrangling is needed to create our dataset. data_topStats is a list with 6 elements, each one of those elements is a tibble. The next code chunk removes the Rank column from each tibble, reorders the columns and then makes a full join by all the non-stat variables using reduce() (the reason behind this full join is that not all players have all stats). In the last line of code I replace NA values with zero in the stats variables.
dataset <- data_topStats %>%
# Remove Rank column
map(function(x) select(x, -Rank)) %>%
# Reorder columns
map(function(x) select(x, Season, Position, Club, Player, Nationality, everything())) %>%
# Full join (because not necessarily all players have all stats)
reduce(full_join, by = c("Season", "Position", "Club", "Player", "Nationality")) %>%
# Replace NA with 0 in numeric columns
mutate(across(where(is.numeric), replace_na, replace = 0))This is how the data looks like.
dataset %>%
head %>%
knitr::kable(format = "html", table.attr = "style = \"color: white;\"")| Season | Position | Club | Player | Nationality | Goals | Assists | Minutes Played | Passes | Shots | Fouls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | Brighton and Hove Albion | Shane Duffy | Ireland | 5 | 1 | 3088 | 1305 | 37 | 22 |
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | AFC Bournemouth | Nathan Aké | Netherlands | 4 | 0 | 3412 | 1696 | 25 | 28 |
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | Cardiff City | Sol Bamba | Cote D’Ivoire | 4 | 1 | 2475 | 550 | 22 | 35 |
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | Wolverhampton Wanderers | Willy Boly | France | 4 | 0 | 3168 | 1715 | 24 | 29 |
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | Everton | Lucas Digne | France | 4 | 4 | 2966 | 1457 | 34 | 39 |
| 2018/19 | DEFENDER | Wolverhampton Wanderers | Matt Doherty | Ireland | 4 | 5 | 3147 | 1399 | 46 | 30 |
parallel Framework
The framework described here is an approach to working in parallel with RSelenium.
First, we load the libraries we need.
# Load libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(parallel)The function defined below stops Selenium on each core.
# Define function to stop Selenium on each core
close_rselenium <- function(){
clusterEvalQ(clust, {
remDr$close()
rD$server$stop()
})
system("taskkill /im java.exe /f", intern=FALSE, ignore.stdout=FALSE)
}We determine the number of cores we’ll use. In this example, I use four cores.
# Determine cores
# Number of cores in your computer
n_cores <- detectCores()
# It's recommended to always leave at least one core free
# clust <- makeCluster(n_cores - 1)
# I decided to make an example using 4 cores.
clust <- makeCluster(4)We have to list the ports that are going to be used to start Selenium.
# List ports
ports = list(4567L, 4444L, 4445L, 5555L)We use clusterApply() to start Selenium on each core. Pay attention to the use of the Superassignment operator. When you run this function, you will see that four chrome windows are opened.
# Open Selenium on each core, using one port per core.
clusterApply(clust, ports, function(x){
library(tidyverse)
library(RSelenium)
library(rvest)
# Pay attention to the use of the Superassignment operator.
rD <<- RSelenium::rsDriver(
browser = "chrome",
chromever = system2(
command = "wmic",
args = 'datafile where name="C:\\\\Program Files (x86)\\\\Google\\\\Chrome\\\\Application\\\\chrome.exe" get Version /value',
stdout = TRUE,
stderr = TRUE) %>%
stringr::str_extract(pattern = "(?<=Version=)\\d+\\.\\d+\\.\\d+\\.") %>%
magrittr::extract(!is.na(.)) %>%
stringr::str_replace_all(pattern = "\\.", replacement = "\\\\.") %>%
paste0("^", .) %>%
stringr::str_subset(string = binman::list_versions(appname = "chromedriver") %>%
dplyr::last()) %>%
as.numeric_version() %>%
max() %>%
as.character(),
port = x
)
# Pay attention to the use of the Superassignment operator.
remDr <<- rD[["client"]]
})This is an example of pages that we will open in parallel. This list will change depending on the particular scenario.
# List element to iterate with parallel processing
pgs <- list("https://www.google.com",
"https://www.nytimes.com",
"https://www.ft.com")Use parLapply() to work in parallel. When you run this, you will see that each browser opens one website, and one is still blank. This is a simple example, I haven’t defined any scraping, but of course you can!
# Define iteration
parLapply(clust, pgs, function(x) {
remDr$navigate(x)
})when you are done, stop Selenium on each core and stop the cluster.
# Close Selenium on each core
close_rselenium()
# Stop the cluster
stopCluster(clust)Observation: Sometimes, when working in parallel some of the browsers close for no apparent reason (or at least a reason that I don’t understand).
Miscellaneous
Workaround browser closing for no reason
Consider the following scenario: your loop navigates to a certain website, clicks some elements and then gets the page source to scrape using rvest. If in the middle of that loop the browser closes, you will get an error (for example, it won’t navigate to the website, or the element won’t be found). You can work around these errors using tryCatch(), but when you skip the iteration where the error occurred, when you try to navigate to the website in the following iteration, an error would occur again (because there is no browser open!).
You could, for example, use remDr$open() in the beggining of the loop, and remDr$close() in the end, but I think that will open and close many browsers and make the process slower.
So I created this function that handles part of the problem (even though the iteration where the browser closed will not finish, the next one will and the process won’t stop).
It basically tries to get the current URL using remDr$getCurrentUrl(). If no browser is open, this will throw an error, and if we get an error, it will open a browser.
check_chrome <- function(){
check <- try(suppressMessages(remDr$getCurrentUrl()), silent = TRUE)
if ("try-error" %in% class(check)) remDr$open(silent = TRUE)
}Closing Selenium
Sometimes, even if the browser window is closed, when you re-run rD <- RSelenium::rsDriver(...) you might encounter an error like:
Error in wdman::selenium(port = port, verbose = verbose, version = version, :
Selenium server signals port = 4567 is already in use.This means that the connection was not completely closed. You can execute the lines of code below to stop Selenium.
remDr$close()
rD$server$stop()
system("taskkill /im java.exe /f", intern=FALSE, ignore.stdout=FALSE)You can check this. StackOverflow post for more information.
Wrapper Functions
You can create functions in order to type less. Suppose that you navigate to a certain website where you have to click one link that sends you to a site with different tabs. You can use something like this:
navigate_page <- function(CSS_ID, CSS_TAB = NULL){
remDr$navigate("WEBSITE")
webElem <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector", CSS_ID)
webElem$clickElement()
if (!is.null(TAB)){
tab <- remDr$findElement(using = "css selector", CSS_TAB)
tab$clickElement()
}
}Observation: this function is theoretical, it won’t work if you run it.
I won’t show it here, but you can create functions to find elements, check if an element exists on the DOM (Document Object Model), try to click an element if it exists, parse the data table you are interested in, etc. You can check this StackOverflow for examples.
Resources
The following list contains different videos, posts and StackOverflow posts that I found useful when learning and working with RSelenium.
The ultimate online collection toolbox: Combining RSelenium and Rvest ( Part I and Part II ). If you know about
rvestand just want to learn aboutRSelenium, I’d recommend watching Part II. It gives an overview of what you can do when combiningRSeleniumandrvest. It has nice an practical examples. As a final comment regarding these videos, I wouldn’t pay too much attention to setting up Docker because at least I didn’t need to work that way in order to getRSeleniumgoing. In fact, at least now, getting it going is pretty straightforward.RSelenium Tutorial: A Tutorial to Basic Web Scraping With RSelenium. I found this post really useful when trying to set up
RSelenium. The solution given in this StackOverflow post, which is mentioned in the article, seems to be enough.Dungeons and Dragons Web Scraping with rvest and RSelenium. This is a great post! It starts with a general tutorial for scraping with
rvestand then dives intoRSelenium. If you are not familiar withrvest, you can start here.RSelenium Tutorial. This post might be helpful too.
RSelenium Package Website. It has more advanced and detailed content. I just took a look to the Basics Vignette.
These StackOverflow posts helped me when working with dropdown lists:
RSelenium: server signals port is already in use. This post gives a solution to the “port already in use” problem. Even though is not marked as best, the last line of code of the second answer is useful.
Data Scraping in R. Thanks to this post I found the Premier League Stats website, which was exactly what I was looking for to write a post about
RSelenium. Also, I took some hints from the answer marked as best.CSS Tutorials: